Vanadium Foil Price & List
| Spec. |
Thickness (mm) |
Width (mm) |
Length (mm) |
| V-F010 |
0.01 |
≤300 |
≥100 |
| V-F020 |
0.02 |
≤300 |
≥100 |
| V-F050 |
0.05 |
≤300 |
≥100 |
| V-F100 |
0.10 |
≤300 |
≥100 |
| V-F200 |
0.20 |
≤300 |
≥100 |
| Customizable |
Customizable |
Customizable |
Customizable |
Note: We provide customized service. If you don't find the foils you want, please send us an email directly. We can customize it according to your requirements.
Vanadium is a silver gray metal. Vanadium belongs to VB group in the periodic table of elements with atomic number of 23 and atomic weight of 50.9414. Its melting point is 1890 ± 10 ℃, and its boiling point is 3380 ℃. Pure vanadium is hard, nonmagnetic and ductile. Vanadium foil is an ultra-thin vanadium foil made from powder metallurgy
vanadium rods or vanadium plate stock through a series of rough rolling, medium rolling, and finishing rolling into vanadium foil of different thicknesses, and then subjected to annealing of the finished product. It is widely used in corrosion resistance industry, coating industry and other fields.
Vanadium foil is a foil-shaped material made primarily from high-purity metallic vanadium (chemical symbol V), produced through processes such as rolling or vacuum deposition. It does not possess the broad industrial versatility of nickel foil, nor does it exhibit a single decisive nuclear property like hafnium foil. However, owing to its unique combination of physical and chemical properties, vanadium foil plays a critical role in a limited number of cutting-edge technological fields.
Core Physical and Chemical PropertiesBasic parameters:Vanadium is a silver-gray transition metal that is relatively soft and highly ductile. It has a density of approximately 6.11 g/cm³, a melting point of 1890 °C, and an electrical resistivity of about 25 μΩ·cm.
Key characteristics:The core value of vanadium foil lies in its overall performance balance:
Low neutron absorption cross section: This property forms the basis of its applications in the nuclear energy field. In contrast to hafnium, which strongly absorbs neutrons, vanadium is essentially “transparent” to neutrons and has a very small neutron capture cross section.
Excellent resistance to radiation-induced swelling: Under intense radiation environments, vanadium alloys can maintain long-term structural integrity, resisting swelling and embrittlement caused by radiation damage.
Good high-temperature strength and corrosion resistance: Within certain temperature ranges, vanadium exhibits good mechanical strength and resistance to corrosion by liquid metals.
Purity as a determining factor: The performance of vanadium foil is highly dependent on its purity. Trace impurities such as oxygen, nitrogen, and carbon can significantly embrittle the material; therefore, high-purity vanadium foil (e.g., 99.7%, 99.9%, or higher) is a prerequisite for practical applications.
Vanadium Foil Application
The applications of
vanadium foil are highly concentrated in advanced technological fields that impose extremely demanding requirements on material performance. Its main application directions are as follows:
1. Nuclear Energy: A Key Candidate Structural Material for Future Fusion PowerThis represents the most strategically significant current and future application of vanadium foil, primarily in nuclear fusion reactors.
Application scenarios:In the design of facilities such as the International Thermonuclear Experimental Reactor (ITER) and future commercial fusion reactors, plasma-facing components including the first wall and blanket are exposed to extremely harsh environments involving high temperatures, high neutron flux, and plasma erosion. Vanadium-based alloys (such as V-4Cr-4Ti) are among the most promising candidate materials for these critical structural components.
Mechanism of action:The low-activation characteristics of vanadium alloys (resulting in radioactive waste with short half-lives after irradiation), their excellent resistance to neutron irradiation–induced swelling, and their good compatibility with liquid lithium (used for tritium breeding and cooling in blankets) make them key materials for achieving safe and efficient fusion energy. Vanadium foil plays an important role in the development, testing, and fabrication of such alloys.
2. Aerospace and Advanced Alloy ApplicationsAlloying additive:Vanadium is an important microalloying element in steels and titanium alloys. When introduced in the form of vanadium foil or vanadium alloys, it can significantly refine grain size and enhance strength, toughness, and high-temperature performance. Such advanced alloys are widely used in critical components including aircraft engine blades, rocket casings, and landing gear.
High-temperature components:Based on the inherent high-temperature performance of vanadium alloys, vanadium foil or thin sheets can be used to manufacture certain high-temperature components or serve as substrate materials for coatings in specialized environments.
3. New Energy and Frontier Scientific ResearchEnergy storage batteries:In all-vanadium redox flow batteries, vanadium foil can be used as a substrate or coating material for electrode current collectors. In addition, in the research and development of new battery systems such as lithium-ion batteries, vanadium oxides or vanadium-based alloys are being investigated as high-performance electrode materials, with vanadium foil serving as a precursor material for their preparation.
Superconducting materials:Vanadium is an important superconducting element; for example, A15-structured compounds such as V₃Si and V₃Ga exhibit relatively high superconducting critical temperatures. Vanadium foil is one of the key raw materials for the fabrication of superconducting wires and thin films used in applications such as high-energy particle accelerators and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) magnets.
Functional thin films and coatings:By using techniques such as sputtering and evaporation, vanadium foil can serve as a target material for depositing vanadium, vanadium nitride, and related hard coatings, optical films, or functional thin films on various substrates, which are widely applied to tools, molds, and precision optical components.
Vanadium Foil for Scientific Research
Vanadium foil for scientific research is often used in certain specific scientific experiments or research due to its small size and small quantity. It is generally cut from rolled vanadium foil. We can provide vanadium foil for scientific research. Dimensions can be tailored according to requirements.
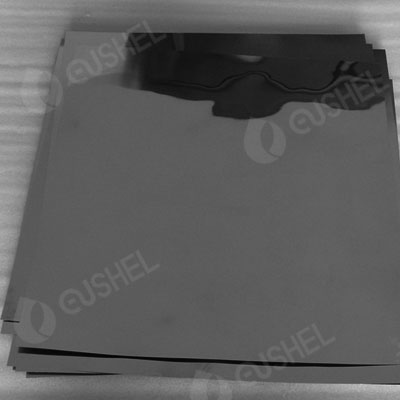

| Spec. |
Thickness (mm) |
Width (mm) |
Length (mm) |
| V-F050100 |
0.05 |
100 |
100 |
| V-F100100 |
0.10 |
100 |
100 |
| V-F200100 |
0.20 |
100 |
100 |
| Customizable |
Customizable |
Customizable |
Customizable |
Industrial Grade Vanadium Foil
Industrial grade vanadium foil is mainly used in industrial fields in batches. The details are as follows:
1. Superalloy of atomic industrial, and aviation;
2. Used for chemical equipment electronic materials, parts, analysis of the standard sample;
3. Used as shielding materials.
| Spec. |
Thickness (mm) |
Width (mm) |
Length (mm) |
| V-F010 |
0.01 |
≤300 |
≥100 |
| V-F020 |
0.02 |
≤300 |
≥100 |
| V-F050 |
0.05 |
≤300 |
≥100 |
| V-F100 |
0.10 |
≤300 |
≥100 |
| V-F200 |
0.20 |
≤300 |
≥100 |
| Customizable |
Customizable |
Customizable |
Customizable |
Vanadium Foil Processing Parts
We can customize and process vanadium foil components with special shapes according to customer requirements. Customized according to customer requirements and drawings.
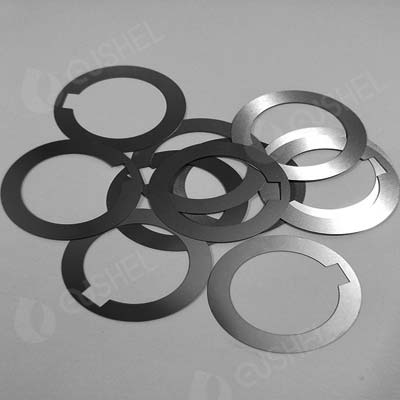


Related Products
Foil Series
Titanium foil refers to an ultra-thin foil produced by repeatedly rolling titanium rods or titanium plate blanks through a rolling mill. Generally speaking, titanium foil, we mainly refer to pure titanium foil. Its corresponding level is Grade 1, Grade 2.
https://www.fushel.com/foil/titanium-foil.html
Molybdenum foil refers to a thin molybdenum foil produced by forging and rolling powder metallurgy molybdenum rods or plates.
https://www.fushel.com/foil/molybdenum-foil.html
Niobium foil is a niobium rod or slab made by niobium powder metallurgy, which is then forged and rolled into niobium thin plates, and finally rolled into thinner niobium foil.
https://www.fushel.com/foil/niobium-foil.html
Tantalum foil is an ultra-thin tantalum foil less than 0.2 mm. Compared with tantalum strip, its thickness is thinner and the production process is more difficult, which is suitable for some occasions where the thickness requirements are relatively thin and high.
https://www.fushel.com/foil/tantalum-foil.html
Tungsten foil is a kind of metal foil made of tungsten. It has a black metallic luster and a smooth and even surface.
https://www.fushel.com/foil/tungsten-foil.html
Rhenium foil is made from rhenium rod or rhenium plate blank by a series of rough rolling, intermediate rolling, and finishing rolling into rhenium foil of different thicknesses, and then annealing the finished product.
https://www.fushel.com/foil/rhenium-foil.html
Hafnium foil is a high purity hafnium metal foil made by special mechanical pressing. It can be used as control rod and protection device of atomic reactor.
https://www.fushel.com/foil/hafnium-foil.html
Nickel foil refers to an ultra-thin nickel foil less than 0.20 mm. Compared with nickel strip, the thickness of nickel foil is thinner, and the production process requirements are higher.
https://www.fushel.com/foil/nickel-foil.html
Related Vanadium Products
Vanadium powder is a refractory metal powder with silver gray appearance. According to different shapes, vanadium powder can be divided into spherical vanadium powder and irregular vanadium powder.
https://www.fushel.com/powder/vanadium-powder.html
Vanadium strip is a thin strip made from high purity vanadium powder, which is pressed into vanadium rods or slabs, then forged, repeatedly rolled and annealed.
https://www.fushel.com/strip/vanadium-strip.html
Vanadium sheet refers to a thin vanadium plate made by a series of processes such as static pressure sintering of vanadium powder.
https://www.fushel.com/sheet/vanadium-sheet.html
Vanadium plate refers to a thick vanadium plate thicker than vanadium sheet.
https://www.fushel.com/plate/vanadium-plate.html
Vanadium bar refers to a vanadium metal bar made by static pressure sintering of high purity vanadium powder. It has various shapes such as round bars, flat bars, and square bars.
https://www.fushel.com/bar/vanadium-bar.html
Vanadium rod refers to a vanadium round bar made from high purity vanadium powder by static pressure sintering followed by a series of processes.
https://www.fushel.com/rod/vanadium-rod.html
Vanadium tube refers to a type of vanadium tube made by static pressure sintering of vanadium powder or processing of vanadium rods.
https://www.fushel.com/tube/vanadium-tube.html
Vanadium wire refers to a small diameter vanadium wire drawn using a vanadium rod.
https://www.fushel.com/wire/vanadium-wire.html
Vanadium sputtering target is a kind of high purity vanadium raw material for sputtering coating. According to the different shapes, vanadium sputtering targets can be divided into circular, rectangular, square, annular, oval, cylindrical, planar, rotatable (rotary) vanadium targets.
https://www.fushel.com/target/vanadium-sputtering-target.html




